
How many AWS re:Invent annual conferences have there been in total? This is the tenth one!
What is the most valuable resource in an organization? Is it physical assets, a portfolio of brands, trademarks and patents, actual money, people, teams, culture? While the response may vary wildly depending on how the discussion partner understands the question, there is one that is a cut above the rest for its propensity to be easy to misinvest and very limited in quantity: time.
With our tools, frameworks, solutions and platforms, we are building experiences that are ever increasingly complex and value-generating. Despite our best efforts, one can do so much in a day. So we pick or develop cleverer tools, sometimes in house, sometimes off the shelf. AWS understood that and listened to their community to identify the largest timesinks of the data industries.
The many facets of data
Data is everywhere and is core to any system. Its growth in size and complexity are exponential. Some of it is structured, immediately searchable and indexable. 80% is not and that is okay. Today, the capacity of a company to gather and extracting insights from raw data is a crucial competitive edge. Understanding the world around is key to sustainability.
Before getting hands on with the data, we need a solid base: each activity and component of our data pipeline must be fully operational, fine-tuned for the job. Setting up a complete environment requires many different skills and can be costly to host and maintain long term. That is why AWS offers services around data that scale with the customers and can serve exotic needs while optimizing costs, performance and reducing operations. These services are made so that specialized engineers can get started in a matter of hours.
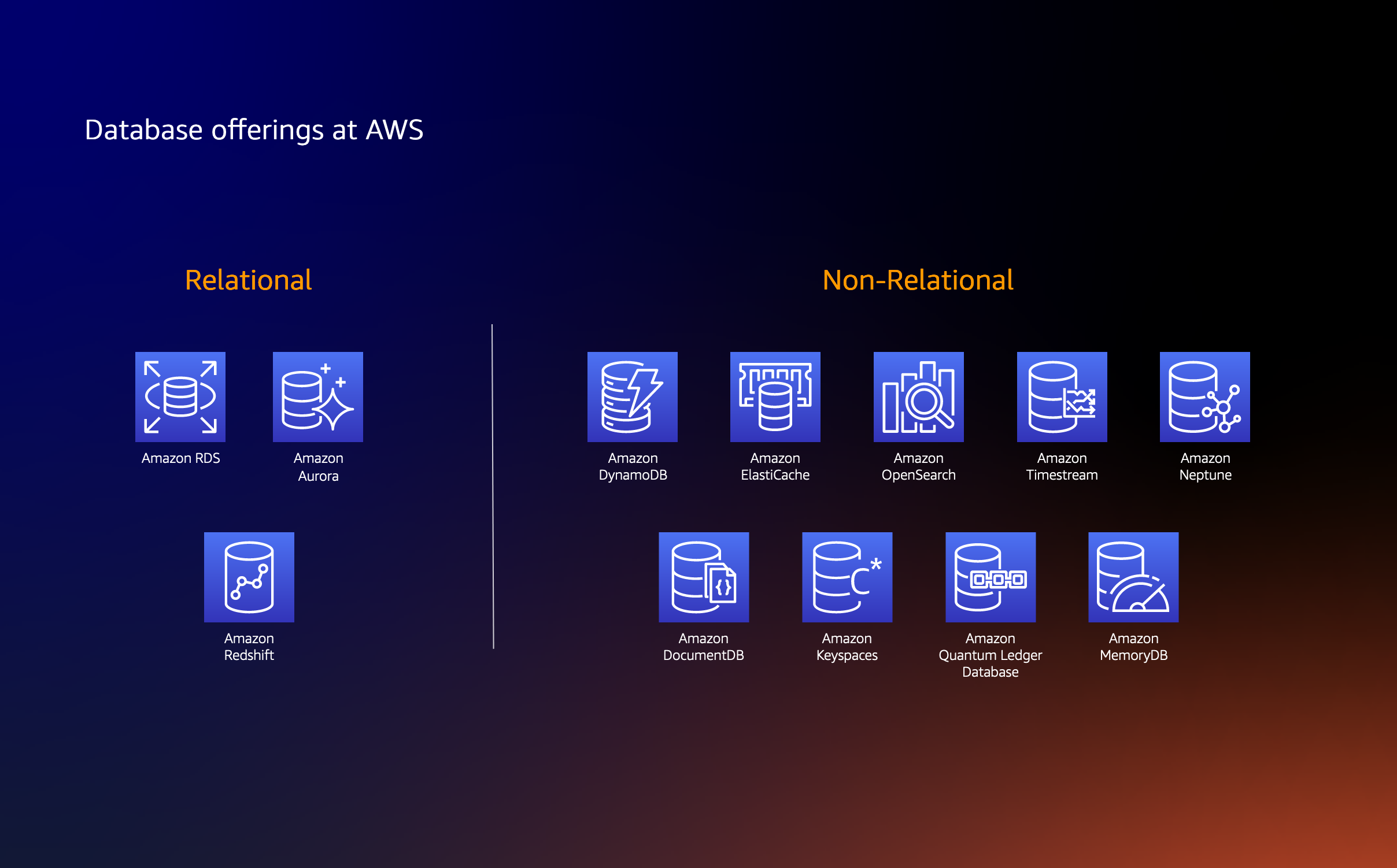
Relational databases and co.
A while ago, we mentioned how Amazon CodeGuru improves the work of development teams by cutting code review time and making relevant security and performance suggestions thanks to an AI trained on massive amounts of codebases. And while capabilities are added from time to time such as secret detection, the solution still has yet to open up to its full potential by supporting more languages and capabilities. In due time.
Can this way of delivering insights be applied to databases as well? There are surely classes of performance issues that are common enough that they deserve their own solution. Introducing Amazon DevOps Guru for RDS, which uses Machine Learning models to detect and diagnose performance and operational issues for Amazon Aurora databases, perform root cause analysis and report remediation suggestions to development teams and DevOps practitioners.
Well used, Amazon CodeGuru and DevOps Guru can help teams save time on classes of issues that are subtle enough that the setup time and cost are easily recovered. However, do you know what can also make you save time? Relying on a database system that you can deeply customize without losing access to integrations and features such as backup and maintenance. Following the announcement of Amazon RDS Custom for Oracle in October of this year, there is now a new version in town with Amazon RDS Custom for SQL Server. Thanks to this new capability, there is no need to create your own SQL Server cluster as soon as you wish to install companions or plugins or fine-tune more than with just parameter groups. You get more control while the service is still managed by AWS!
Finally, if you host sufficiently large serverless applications, you might have DynamoDB tables that contain large amounts of infrequently accessed data. This pattern may for instance be implemented when you need archival tables to soft-delete records from a primary table. Instead of moving the data points to another service like S3, you may now use storage tiers in DynamoDB directly thanks to the Amazon DynamoDB Standard-Infrequent Access table class! Its promise: just like Amazon S3 Standard-Infrequent Access, storage costs are significantly lower while access costs are slightly higher, which makes this solution suitable for tables that don’t change often and have significant enough storage costs.
Mass migrations
If you ever migrated a database, you might have faced difficult decisions such as the instance type and size to choose, how to migrate your data so that the cutover can be smooth, how to guarantee one-to-one feature parity with your old system, etc. Now imagine a project where tens, hundreds or thousands of databases must be migrated to AWS. Migrating and ensuring that everything works identically on the destination is a herculean effort. AWS has a service for that: AWS Database Migration Service, which manages database replication to ensure smooth migrations. But this service covers individual databases and would only slightly alleviate the pain in the case of massive migrations. We need more.
At this scale, you need more than just replicating data: you need an inventory of what you need to migrate, to choose the destination hardware configuration, to ensure that configurations are identical and be able to change platforms for some database. This is now possible thanks to AWS DMS Fleet Advisor which handle database migrations from discovery to cutover for the low price of free. Note that this capability is in Preview though.
With this announcement also comes AWS DMS Studio, a new console experience that gives an overview to migration projects and presents tools to get you through each phase, including schema conversion and code modifications.
Data lakes
Diving into data lakes is like recounting a story. AWS hosts thousands of data lakes and most of them chose Amazon S3 as their platform. Amazon S3 is particularly well suited for this usage since it can massively scale, has excellent durability, availability and performance and can integrate with other AWS services as well as partner solutions! Nevertheless, building a data lake on Amazon S3 requires handing out very specific access to certain contents to certin groups of users. User and system access is the complex part of the data lake today, that is why there are services like AWS Lake Formation to provide a framework to reduce the efforts needed in building a state of the art data lake.
Data lake data is messy, analyzing it requires tools too and the most basic of them for that purpose is Amazon Athena, which can natively connect to S3 buckets and extract information from your objects. Pay as you go, serverless, SQL-like, Athena can really get you started with analyzing your data in a matter of the time it takes to respond to your queries, that is seconds! In case your need is more specific, you should definitely try onf of the other analytics options such as Amazon MSK, Amazon Kinesis, Amazon EMR and Amazon Redshift.
Speaking of Amazon Redshift, did you know that you can automatically compress columns to save space, that you can scale writes, that you can enable a query accelerator and that you can also automatically generate Machine Learning models from the data stored in your database? Such is the value proposition of Amazon Redshift.
Finally, this story ends with the end users, your business analysts and deciders which explore and visualize the data using Business Intelligence tools like Amazon QuickSight. Thanks to Amazon QuickSight Q which uses the power of Natural Language Understanding, non-experts can now “ask questions to the data” and get relevant answers in return!
Machine Learning
Machine Learning is as powerful as it is time consuming. Artificial Intelligence is all around us in recommendation engines, virtual assistants, fraud detection services and even in our cars now. Learning to harness the power of Machine Learning gives businesses a significant competitive edge, despite the investment to get at that stage.
What exactly is time consuming? Assuming you have enough data to create a model, you will need to ensure that it is ready, that is structured homogeneously, unbiased and correctly labeled so that you can use it for training and evaluating your model. This preparation step is far from effortless and requires skilled engineers to execute low-value tasks. While most of the preparation work can be accomplished using tools such as Amazon SageMaker Data Wrangler, the labeling step must be done by humans in certain cases; you cannot use an artificial intelligence to produce accurate labels from the dataset, otherwise you would not need to train a Machine Learning model for that use case in the first place! What if… we could use one to reach sufficient accuracy and then ask humans to verify or rectify mistakes?
Amazon SageMaker Groud Truth is the data labeling offering from AWS. This service allows customers to send data to label to teams of Labelers either internal, third-party or Amazon Mechancal Turk. This basically moves the data labeling from your organization to people used to label data. Today, there is a better way: with Amazon SageMaker Ground Truth Plus, after an initial setup phase, the dataset is pre-labeled using a Machine Learning model, then a workforce completes the last steps of data labeling. This process ensures a higher level of quality while simplifying the whole process and reducing costs!
Another pain point concerned the infrastructure surrounding the training task: managing the Notebooks infrastructure, training time, choosing the right instance size for the inference step. You can also choose not to choose an instance size for the inference step, actually. This option is in Preview and might be suitable for infrequent inference tasks.
Experience
A wise person once said that a pristine backend accounts for nought if your customer cannot use your frontend. Ponder this: you have a tool capable of searching through your knowledge bases and retrieving accurate and relevant results but you have to ask teams to developers to integrate it to your internal platforms with relative success. This specific last-mile delivery issue concerns Amazon Kendra, which launched its own Experience Builder.
Customer support is also part of the experience and having well designed flows and the right tools at your disposal can mean a lot to your customers, customer support representatives and ultimately your business. This is where AWS Chatbot and Amazon Connect shine. The former helps teams building chatbots while the latter is in fact a framework to build a call center as a service!
Designing chatbot conversations is no easy feat. It is akin to designing actual conversations by running every possibility in your head. Conversation design is a skill to and Machine Learning can help with that using Natural Language Understanding to analyze conversation transcripts and identify common traits. This can accelerate chatbot development and is a Preview feature of Amazon Lex Automated Chatbot Designer.
As for Amazon Connect, it is now possible to automate call summarization, a feature that automatically creates a summary of a customer support conversation and identifies key elements such as issues and outcomes. This will give the opportunity for customer support representatives to spend less time writing these summaries and reading transcripts in case they are not clear enough. Managers can skim the summary to get the context of a conversation without listening to the recording as well.
Education
To end on more positive notes, over the course of this presentation there have been announcements oriented towards non-technical people. These new capabilities enable using the same tools as domain experts such as DBAs or Data analysts (think Amazon SageMaker Canvas) without necessitating the full knowledge from these positions. In other words, development teams and deciders can claim back some degree of autonomy and that expert teams will have less to worry about in the long run.
Let’s turn to new opportunities now: we need more data scientists to make sense of the data around us. And so AWS started initiatives including the AWS DeepRacer Leagues which have just been renewed for 2022 and the AWS AI & ML Scholarship Program. Both will enable the next generation of data and machine learning specialists with a focus on underserved and underrepresented students.
Your turn now
With all of these announcements, it is clear that AWS wants expert contributors and teams to concentrate on their expertise rather than toil. These are mostly everyday quality of life improvements that will translate to faster value creation, experimentation and delivery on AWS.
We are still not done yet! Check back soon for new announcements on this week of re:Invent. Or check out the AWS Blog if you cannot wait!